We know from our previous post what is diode? This article is about different types of diode. When comes to understanding of power circuit in your electronic items, diode is key component to learn first. There are several types of diode with different functionality, voltage and current ratings. Let’s discuss them.
Signal diodes: –
Signal or standard diodes are simplest P-N junction diodes. According to current carrying capacity and power ratings standard diode is of two types; small signal and large signal diode. These diodes are present in voltage clipping and switching applications. The 1N4148, for example, has VF = 1V and IF = 200mA, also 1N914 has VF = 1V and IF = 300mA.
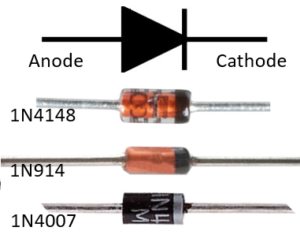
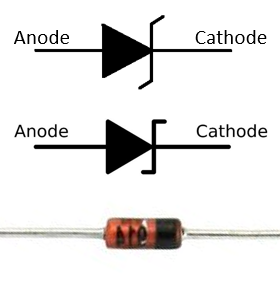
The large signal diodes are also known as rectifier or power diode. They have higher voltage and current rating to be used in power supplies. The 1N4007, for example, has VF = 1.1V and IF = 1A.
Zener diodes: –
Zener diode is distinct from other types of diode, as it usually conduct with reverse current. In forward bias, it works as normal diode. In reverse bias, when reverse current through Zener diode is increase to rated value, the voltage drop across diode becomes steady. This voltage drop is known as zener voltage (reverse breakdown voltage). The current can flow in reverse direction, when increase in voltage crosses zener voltage. The Zener diode creates known reference voltage for voltage regulation, waveform clipping in regulated power supply.
Let’s understand working of Zener diode with circuit simulation. Consider following example of voltage regulator with 30V AC source and Zener diode (with VZ = 15V, VF = 0.7V).
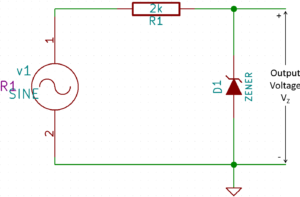
In above circuit, Zener diode is reverse bias for positive half cycle. The voltage more than 15V will turn ON diode. The increases in input voltage beyond 15V will simply appear across the series resistor. As source is AC, the output voltage (VZ ) is constant for a certain amount of time till the positive voltage starts decreasing.
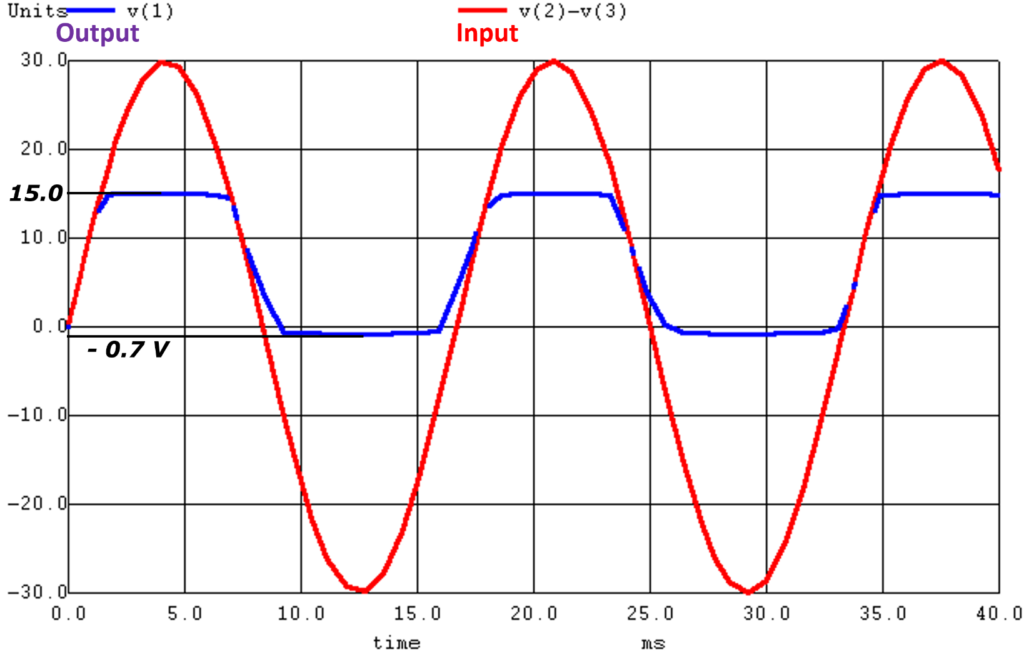
In negative half cycle, Zener diode is forward bias. The increase in negative voltage till forward threshold voltage (VF), turns ON Zener diode. The negative side of the output voltage is at threshold voltage equal to 0.7V.
The examples of Zener diode are 1N746, 1N4728A etc. The important factors for selecting Zener diode are source voltage, load voltage, load current of circuit. Zener diode is available in variety of voltage and power ratings.
Light Emitting Diodes: –
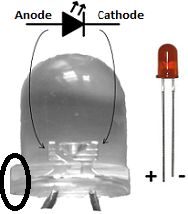
LED is a P-N junction diode which emits light when turned ON. Similar to standard diode LEDs are unidirectional and have forward voltage rating (voltage required to light up). The forward voltage (VF) rating of LED is higher than standard diode. The VF depends on the color LED emits and the color of LED depends on its material composition. The forward current (IF) is second important parameter for LED. It is the amount of current going through an LED and it is directly proportional to LED brightness. The value of IF is in milliamps; but increase in IF value beyond specified limits damages LED. This is the reason behind always using a resistor in series with LED.
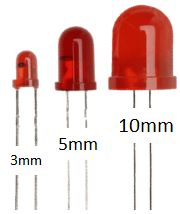
The polarity of LED is important in circuit design. The polarity of LEDs can be identified by observing it carefully. The long terminal or rounded side is anode and short terminal or flat side is cathode. LED comes in different sizes and as per size LEDs are distinguished with diameter (expressed in millimeter-mm). The 3 mm, 5 mm and 10 mm LED are intended to be used for indication, illumination and indication/illumination purpose respectively.
The primary factors while selecting an LED are size, color and purpose. The LED datasheet conains informaton about wavelength (tells exactly what color will LED emit), Forward voltage – VF (voltage required to turn ON LED at some IF) , reverse current/voltage ratings and physical dimensions etc.
Schottky diodes: –
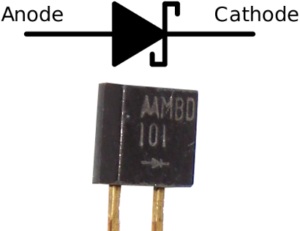
Schottky diode is unique semiconductor diode, formed by the metal-semiconductor junction. This special construction gives lower forward voltage drop (within 0.15-0.40V) which gives fast switching speed. The schottky diodes have low reverse voltage ratings (typically 50 V or less), relatively high reverse leakage current and high cost. Schottky diodes with high reverse voltage always have high forward voltage drop than other types of diode. Schottky didoes are suitable for low voltage applications due to their less power dissipation. Some other applications of schottky diodes are photovoltaic (PV) system, voltage clamping circuits, RF circuits.
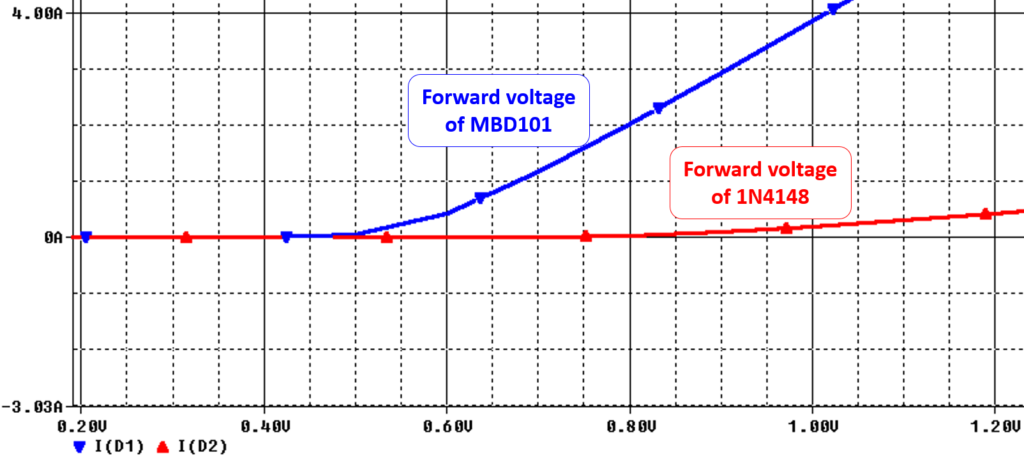
Let’s compare schottky diode MBD101 with standard P-N junction diode 1N4148 with following circuit.
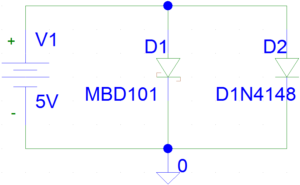
The datahseet specifications of MBD101 and 1N4148 shows typical forward voltage of 0.5V and 1V respectively. We can compare these parameters by software simulation as shown below.
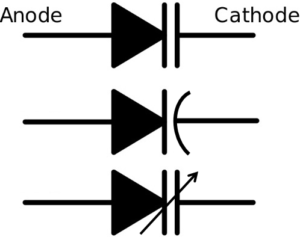
Varactor diodes: –
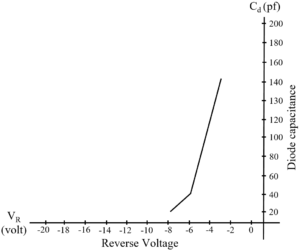
Varactor diode is a unique type of diode. Its P-N junction capacitance can be altered with an applied reverse voltage. Varactor diode is known as Varicap / Tuning diode / Variable capacitance diode. The P and N type region in diode act as charged plates and depletion region as dielectric or insulator. The change in reverse bias voltage changes diode capacitance. This effect is similar to changing the distance between the plates of the capacitor. Varactor diode is purposely utilize in reverse bias. The following mathematical relation explains working of Varactor diode.
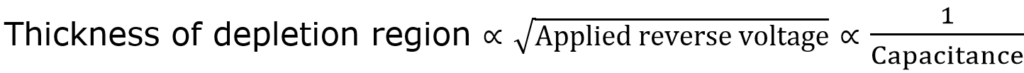
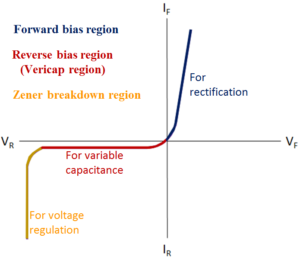
In forward bias, Varactor diode is not much useful and offers very low resistance. The important technical parameters for selecting Varactor diode are Interterminal capacitance or diode capacitance, Reverse breakdown voltage, Capacitance ratio etc. The Varactor diode has low-noise characteristics, low cost, high reliability and small size. Varactor diode is present in Tuning circuit of oscillator, as RF phase shifter, in Variable resonance tank LC circuit etc. An example of varactor diode is NTE618.
This is it for this post. I believe now you’re familiar with different types of diode and their significance. In next post, we’ll learn about reverse current protection using diode. Thanks for reading.
 BINARYUPDATES.COM EMBEDDED SYSTEMS TRAINING
BINARYUPDATES.COM EMBEDDED SYSTEMS TRAINING